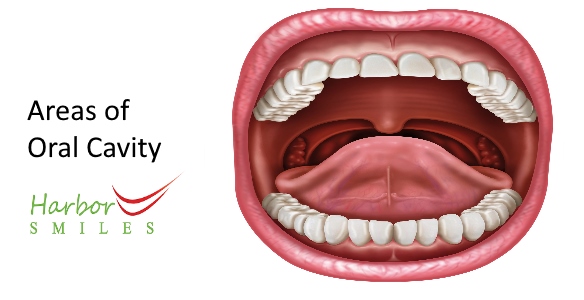
The oral cavity pertains to the mouth, consisting of the lips, the internal lining of the lips and cheeks, the lower and upper gums, the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, the floor of the mouth under the tongue, the little area behind the wisdom teeth, and the bony roof of the mouth. It houses the teeth and tongue and receives salivary gland secretions.
Table of Contents
Where is the Oral Cavity located?
The oral cavity is located at the front of the face, below the nasal cavities. It has a side wall, a ceiling, and a floor.
What comprises the Oral Cavity?
There are two distinct sections to the oral fissure:
- the region between the cheeks, lips, and teeth, often referred to as the oral vestibule.
- the area in-between teeth, sometimes referred to as the mouth.
What is the function of the Oral Cavity?
The mouth’s main purpose is to start the digestive process. After obtaining the meal, it is next sliced into pieces. The particles are then combined with saliva to start the swallowing process.
How large is the Oral Cavity?
A man’s oral fissure typically holds 71.2 ml of fluid as opposed to a woman’s 55.4 ml.
Why is the Oral Cavity essential?
Effective speech production, breathing, and the ingestion and digestion of food and liquids all depend on the mouth. The bulk of the mouth’s structures, the teeth, crush and shatter food into little pieces to make it easier to digest.
What is the Oral Cavity proper?
The masticatory mucosa (hard palate and gingiva), soft palate, inferior surface, lining mucosa (cheeks, lips, mouth floor, and alveolar mucosal surface), and specialized mucosa all cover the inside of the mouth (back of the tongue).
What is meant by areas of the Oral Cavity?
Regions of the oral cavity are used as codes to specify the kind of dental treatment that was done.